In a field traditionally associated with compassion and care, the rise of robotics in healthcare might make you wonder if the doctor’s office is about to become a cold and sterile place. As far as sterility goes, that may be true. Otherwise, robotics may actually enhance healthcare. These devices help doctors perform surgeries more accurately, improve patient care, and ease the workload on healthcare workers.
The healthcare industry may also face a significant shortage of physicians and nurses in the future. Robotics can help fill that gap and free up healthcare providers for the more important work—caring.
Let’s explore the nuts and bolts of how robotics is changing healthcare.
How healthcare robotics work
Robots in healthcare come in all shapes and sizes. Some are large mechanical arms with attached surgical equipment. Others are motorized carts that find their way through a hospital with a built-in map and a WiFi connection. Still, others augment the human body and use AI to ensure that limbs move as they should. But this writer is partial to the cuddly ones currently helping elderly patients with dementia.
Healthcare robotics is often part of the Internet of Things (IoT) (also known as the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)) and uses artificial intelligence (AI). IoMT links robots together over a network that lets them to gather and store patient data. AI allows robots to have conversations with and respond to patients.
Robotic devices often need a connection to the internet, especially when they provide telemedicine services. Thanks to 5G and fiber internet, connectivity with low latency is now becoming possible.

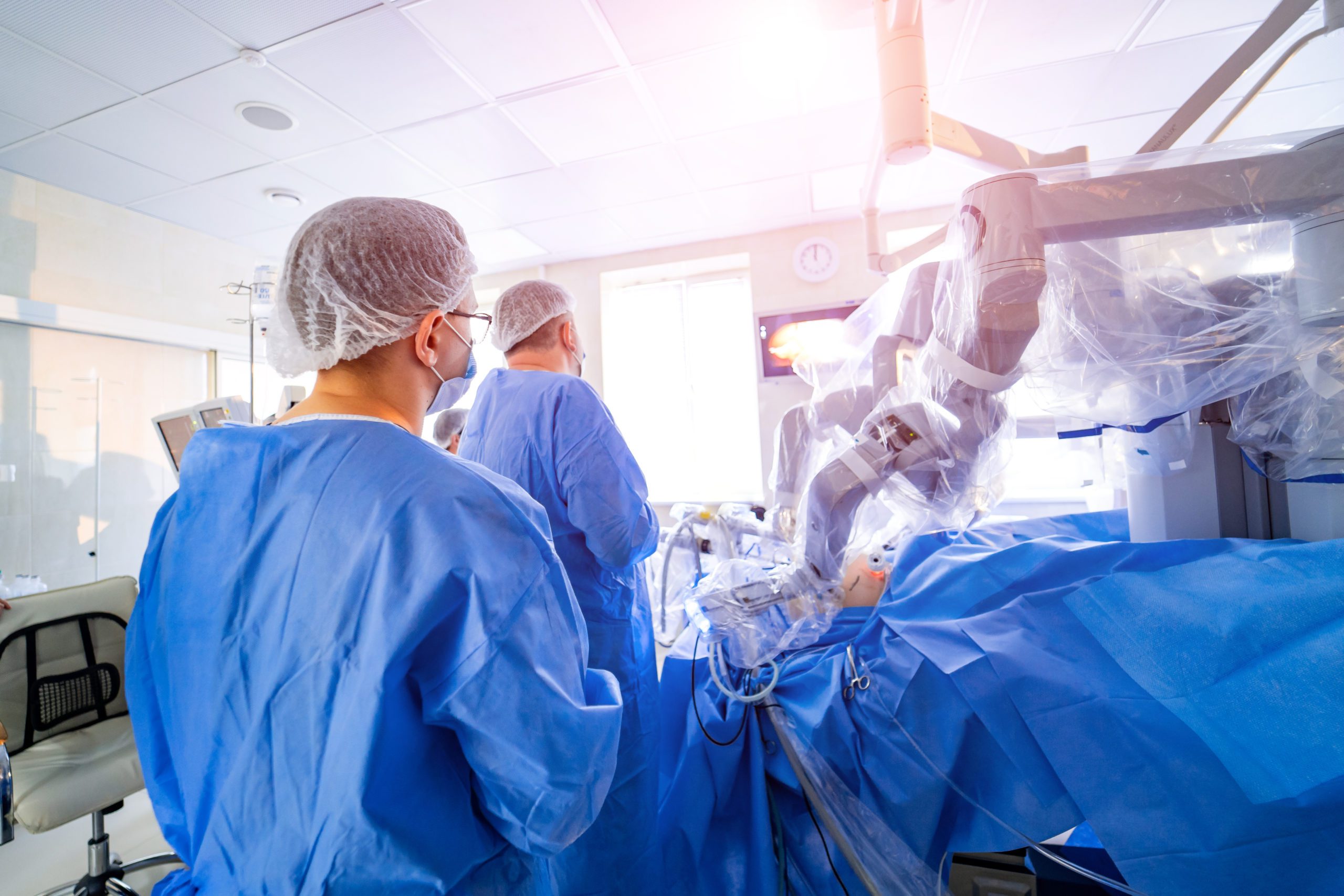
Robotic surgery
When it comes to using robotics in healthcare, surgery is one of the most well-known applications. Among their many benefits, robots can help surgeons stay sharp, giving them better control during operations. They also help post-op patients, or after a severe injury, they can even provide physical support and mobility assistance.
Assisting in surgery
Most robotic surgery is assistive in nature. Doctors can perform surgeries from a distance, including making and closing incisions and precisely implanting medical devices. A computer allows the surgeon to control the robotic arm, and cameras give a more in-depth view, offering high-definition, 3D, and magnification. In some cases, robotic tools perform with greater precision than a human surgeon could on their own.
Robotic surgery also makes healthcare more accessible to rural communities thanks to an internet connection. Doctors are now able to complete surgical procedures from miles away using a robotic arm.
Post-surgery recovery
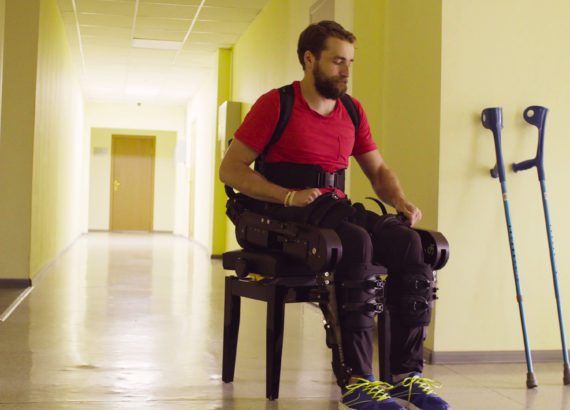
Some robotics, known as exoskeletons, help people recover and regain mobility after surgery or injury. These complex, computerized structures provide support and augment the human body by delivering assistive “muscle” power. Typically, they attach to the lower body. The patient wears a backpack that holds a computer to control the exoskeleton. The high-tech exoskeletal framework is so powerful, it can even help people who have suffered spinal cord injuries walk again.
Patient care and robotics
While the idea of automating care may seem cold, it may actually enhance and improve the patient experience. Robotics can monitor at-risk or chronic patients more frequently than human healthcare providers. Plus, they efficiently monitor vitals and automatically send alerts if issues arise.
Robots are also well-suited to basic, routine tasks that consume a lot of time. This makes them perfect for updating patient records, disinfecting and cleaning rooms, or greeting patients and guiding them to the correct department. Some even provide medication or exercise reminders for elderly patients.
Robots and elderly patients
As the US population ages, the eldercare workforce isn’t keeping up. Healthcare robotics can help.
Some of these technologies and devices may help seniors stay independent longer. Exoskeletons, for example, can assist elderly patients with getting around. Service robots help seniors get items they need or remind them to take medication or to exercise.
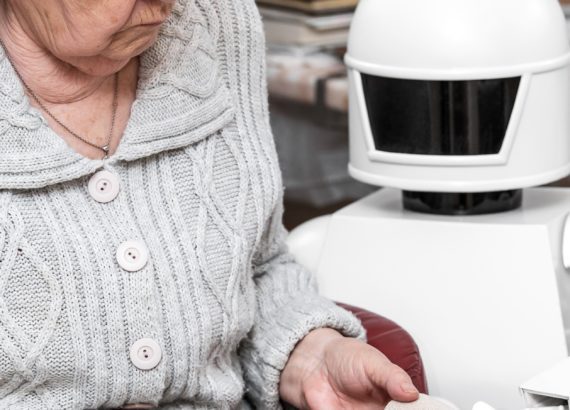
Perhaps most significantly, robotics in healthcare can provide companionship and comfort. Patients with dementia may experience agitation and distress, but a robot can help calm their anxiety. Often, these types of robots come in lovable forms, like a cute puppy or seal that reacts to touch and voice.
Other care robots respond to conversations with patients and obey voice commands in case help is needed.
Healthcare workers and robotics
Robotics benefit healthcare workers, too. They ease heavy workloads and reduce exposure to infectious diseases during patient care.
Shaking up routine
Many healthcare workers choose their profession to help people, but then they become bogged down by routine tasks. Robots can clean hospital rooms in just 20 minutes, deliver meals to patients, monitor vital signs, deliver medications, or take specimens to the lab. They may also be useful in training and educating staff. That leaves the more essential work of empathy and compassion to humans and frees up healthcare workers to serve more patients.
Reducing exposure
Through robotics, the people in healthcare might even minimize their risk and exposure to viruses and bacteria. Much like robotic arms and telemedicine can provide long-distance access to healthcare, these same technologies can allow providers to care for patients remotely in the case of a highly contagious disease or infection. Robots can also perform “the heavy-lifting”—literally. They can move patients, boxes of supplies, and beds, to prevent injury to healthcare workers and decrease physical contact resulting in infection.
No, healthcare robotics won’t replace human healthcare workers
You’re wondering about it, but there’s no need to worry. With a wealth of knowledge about the body and intensive training in providing care, human nurses, physicians, and healthcare workers aren’t going anywhere. AI isn’t currently at a level where it can fully emulate the human mind. Yes, robots can provide some care, but they can’t replicate our most unique quality—empathy.
Instead, healthcare robotics can merely augment and improve the current processes healthcare workers use to provide care.